
The thawing losses of the food industry can be minimized with a controlled thawing process
Breaking the cellular structure of food during the freezing or thawing process reduces the quality of the product and increases losses. However, with a controlled thawing process based on air circulation, the quality of the product can be kept at the same level as a fresh product, reducing the thawing loss.
The thawing of food is a critical stage of the freezing process because it involves the change of ice crystals into thawing water, as well as the reactive action of microbes that were inhibited during freezing.
To reduce the growth of microbes and the thawing loss that occurs during thawing, the thawing process of food should be done carefully and in a controlled manner without breaking the structure of the food.
In the process of food thawing, it is important to know the difference between thawing and tempering (partial thawing)
The terms thawing and tempering are easily confused. The correct terminology is microwave tempering, although in everyday life we often talk about microwave thawing or defrosting. Kometos thawing systems can be used for both thawing and tempering.
Thawing is the process of defrosting the product to 0°C degrees or above, changing the physical state of the product. With tempering, the product remains in the same physical state, only its temperature is changed. For example, when tempering meat, the temperature of the frozen product is raised from -20 degrees °C to -5 degrees °C.
When the product’s surface temperature rises too high, thawing losses occur
When the food surface temperature rises too high during the thawing process, it causes weight and thawing loss. This also breaks the product’s cellular structure.
Breaking the cell structure in the thawing process reduces the quality of the product and increases thawing loss. For example, when tempering meat with water or using excessively warm air, there is a risk that microbes will start to spoil the surface of the meat even before the product has completely defrosted.
In addition to microbiological spoilage, a large temperature difference during tempering increases thawing loss. That means that the product shouldn’t be heated too much. Raimo Niemi, Sales Manager at Kometos, says:
If the food’s surface temperature rises too high, the tissue of the product opens up and drains, for example, meat liquids. The leaking of meat liquids causes, in addition to weight loss, the loss of trace elements and vitamins affecting the taste of the product.
As a reference, the scale of microwave thawing is from -20 degrees °C to -5 degrees °C. If the product’s melting point is exceeded, the microwave will start cooking the product.
– Hot spots mean openings, i.e., empty air gaps inside the product to be thawed. In this case, the product heats up to -5 degrees °C, says Niemi.
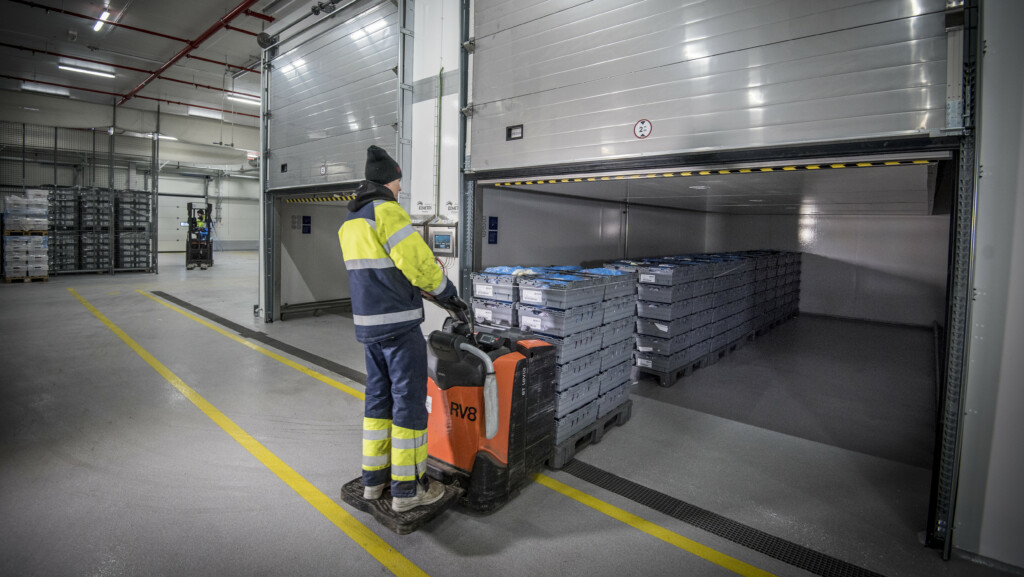

Thawing loss can be minimized with a thawing system that uses air circulation
The Kometos thawing process utilizes heat, controlled air flow, refrigeration technology, humidity, and the “ice bank” formed by the product.
The range of the Kometos thawing system is from -20 degrees Celsius to +4 degrees Celsius, and in special cases even higher. Niemi adds:
In the Kometos thawing process, we get to the plus side without changing the physical state of the product from the original. The change only happens from frozen to thawed.
With the help of air circulation, the products can be tempered quickly and with minimal loss. The temperature of the thawed product remains more even, and the surface temperature doesn’t rise too much remaining unfavorable for the growth of microbes. When the product is thawed with controlled air circulation, its quality, i.e., color, final temperature, and taste remain consistent.
– The result of our thawing process is a high-quality product with minimal loss. With the Kometos thawing systems, the loss of food i.e., the release and evaporation of liquids is minimized to less than one percent, summarizes Niemi.
Compared to the controlled air circulation process, the loss of cold-water thawing, and cold room thawing is up to 4-8%. When using the last two, the quality of the final product also deteriorates due to soluble minerals. Read more about the differences between various thawing methods here.
Concrete examples of thawing results with Kometos’ equipment
Kometos’ thawing systems offer solutions of various sizes for both small and large thawing capacities. Whether you’re thawing 300 or 24 000 kg of product, the systems are equally efficient and maintain minimal thawing loss.
The thawing solutions are suitable for a wide range of products, including meat, poultry, fish, and vegetables. The end result is always a high-quality, evenly defrosted product with matching core and surface temperatures.
Take a look at concrete examples of our customers’ thawing results with different products:
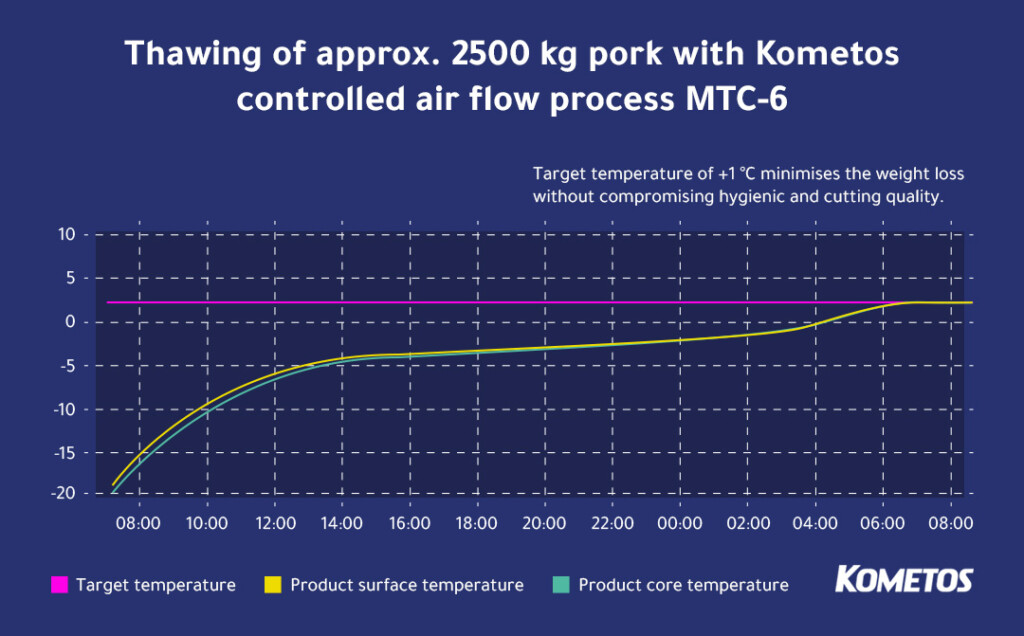
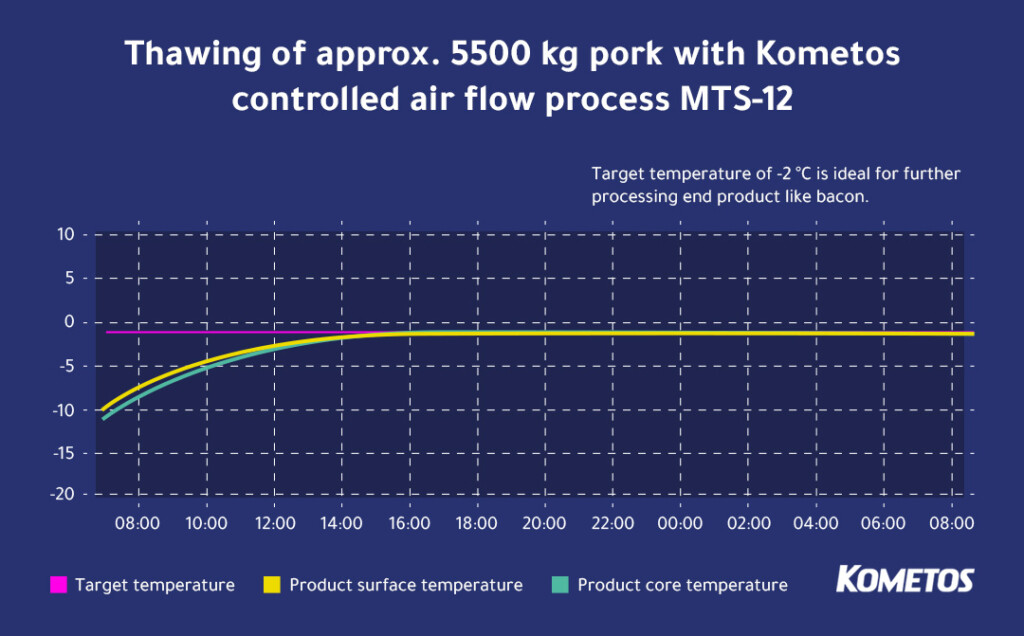
The graphs above illustrate thawing different quantities of pork.
In the first example, pork was thawed from approximately -20°C to above 0°C. The core and surface temperatures of the final product are nearly identical, ensuring the thawed meat maintains consistent quality with minimal waste.
In the second example, the meat was tempered to -2°C. The customer manufactures pork products like bacon. For further processing, -2°C is optimal as it allows for precise slicing.
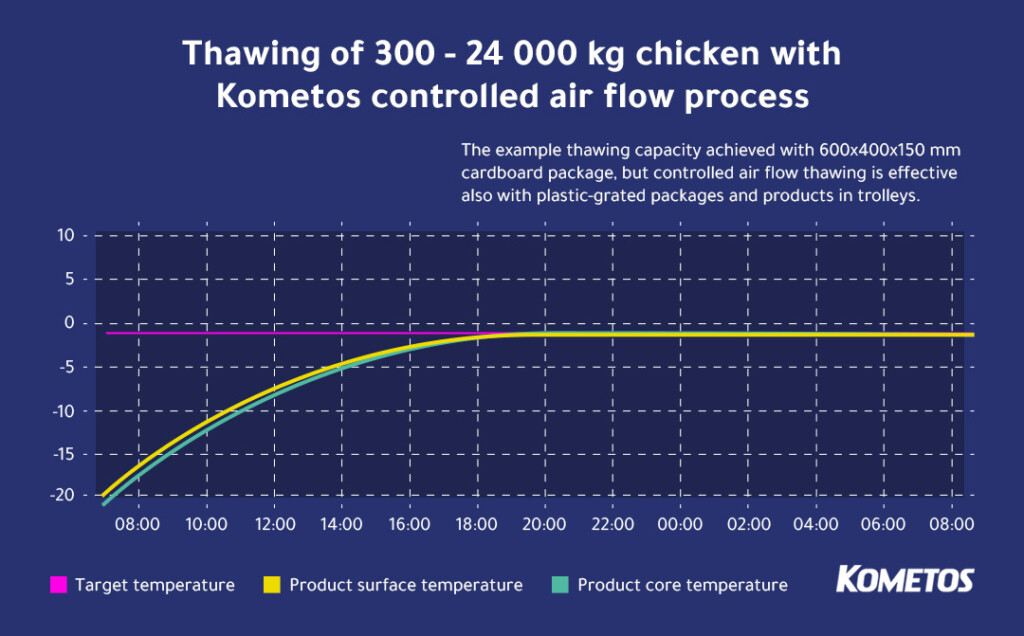
This example shows tempering of varying quantities of chicken. While the meat was in cardboard packaging, the thawing and tempering process would work equally well for products packed in plastic containers or trolleys.
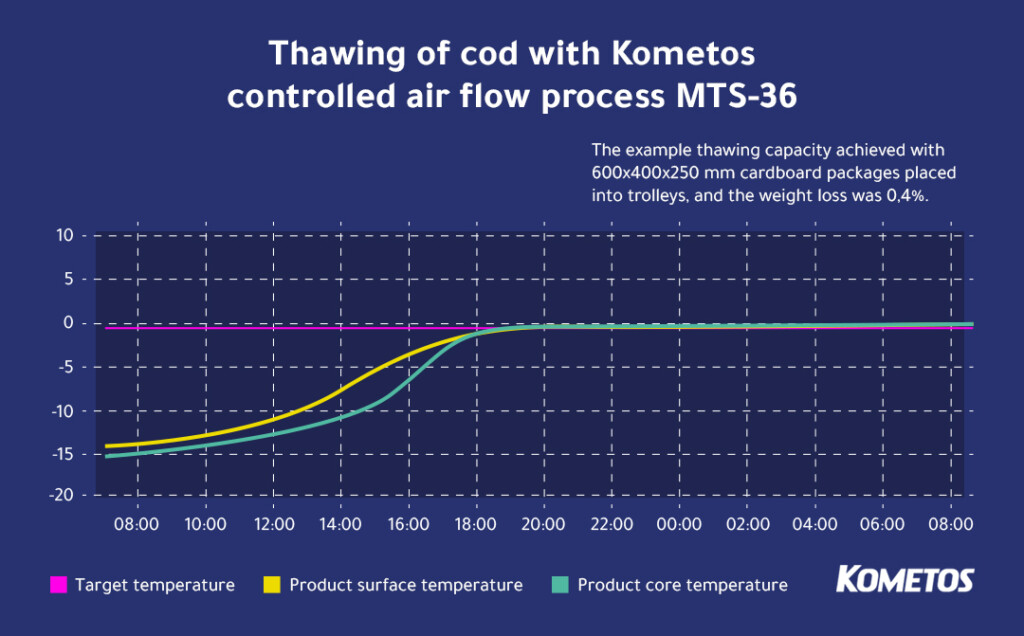
The thawing systems are suitable not only for meat products but also for fish and seafood. This customer’s product is cod. The thawing process keeps weight loss to an absolute minimum: when fish is brought from approximately -15°C to zero, drip losses remain at just 0.4%.




